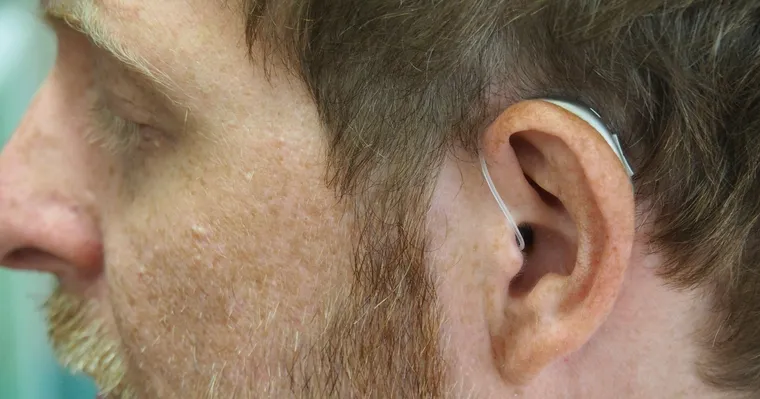
These small, electronic devices amplify sounds for those with hearing loss, opening up a whole new spectrum of auditory perception. They embody a blend of advanced technology and innovative designs, offering a greater degree of customization based on individual needs.
Unveiling the Different Types of Hearing Aids
From a broad perspective, there are three main styles of hearing aids that have been designed to address varying degrees and types of hearing loss: Behind-the-Ear (BTE), In-the-Ear (ITE), and In-The-Canal (ITC). The Behind-the-Ear version houses the technology in a casing that rests behind the ear, with a thin clear tube sending the sound into your ear. In contrast, the In-The-Ear and In-The-Canal models are more discreet, with all components fitted inside a small case that fits either in the outer ear (ITE) or into the ear canal (ITC) itself.
Furthermore, hearing aids are often differentiated by the technology they employ. Analog hearing aids primarily convert sound waves into electrical signals, which are then amplified and sent to your ear. On the other hand, digital hearing aids convert sound waves into numerical codes, amplify them and give the added advantage of fine-tuning the sound. The former is generally less expensive, while the latter offers more features and options. The spectrum of hearing aids also includes over-the-counter models for mild to moderate hearing loss and prescription devices for severe hearing loss.
Matching Your Needs: Tips to Choose the Right Hearing Aid
When you're on the hunt for the right hearing aid, it's crucial to consider a few key factors. The severity of your hearing loss and your specific needs can greatly sway your decision. If your hearing loss is mild to moderate, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids might be a suitable, cost-effective choice. However, for severe hearing loss, prescription aids, which offer a wider range of advanced features and adjustments, are typically recommended. Remember to bear in mind the trade-off between lower hearing aid power consumption and the need for additional accessories.
Consideration should also be given to the style of hearing aid that best fits your lifestyle. There are three basic styles of hearing aids: Behind-the-ear (BTE), Inside-the-ear (ITE), and In-the-canal (ITC). Each design comes with its own set of strengths and potential pitfalls. The BTE design for example, usually employs more advanced technology and is easier to manipulate due to its size. The ITE and ITC designs offer a discreet, inobtrusive option. Assessing your comfort and ease in using them as well as their compatibility with your preferred attire and accessories, can significantly impact your overall satisfaction and hearing aid wearing experience.
Dealing with Hearing Loss: How Hearing Aids Can Help
Hearing aids can be a life-changing solution for those living with sensorineural hearing loss. This condition, caused by damage to the tiny sensory cells in the inner ear, can severely limit an individual's ability to engage in conversations, enjoy their favorite sounds, or comfortably navigate their environment. Thankfully, with the help of a small electronic device known as a hearing aid, these sounds are amplified, thus enabling those who face difficulties with their hearing to interact more effectively with the world around them.
A key advantage of modern hearing aids, especially those utilizing state-of-the-art wireless technology, lies in their connectivity. These advanced appliances not only interact seamlessly with each other but are also capable of effortlessly connecting with your favorite devices such as smartphones. This greatly enhances the quality of life for individuals with hearing loss. Even amidst potential challenges such as background noise or the need for periodic adjustment, the application of auditory models in the design of hearing aids ensures optimized functionality, promoting a more natural auditory experience.